Modernism is the term used to describe the cultural expressions of modernity in relation to the experience of modernity, (much like a design movement or art movement like Cubism, Impressionsism and Surrealism etc).
- without modernism you wouldnt have contemporary design. Up until the 18th century the word 'Modern' in culture was used for direct comparison. The Modern's were superior to the 'classical's'.
- Modern was a progressesion to improve, much like The New Labour party, it was to signify better things.
- Modernism lasted for about 200 years, and there was a rapid change, Paris was the most modern city in 1900.
Modernism cam from the shift in society also known as Urbanisation. Which is when places were no longer rural but became more urban. The city was the most common residence as there were new forms of leisure such as galleries, cinemas and shopping.
Also before Modernity there was a world standardised time, which meant the world ran on the same time, whereas now we have GMT and other countries around the world differ in times.
When Modernity came around it began to move away from religion and spirituality and looked more towards the idea of science in the late 18th century. Society was now secular and the city became the personification of Modernity.
Paris began to become modern yet still kept some of its historical elements.
- Modernity began to shift the ways in which artists responded to the world, the experience of Modernity bacame the man subject within their work.
Work by Caillebotte was focusing on the new living in Modernity and thelifestyle rather then the people themselves.
The Haussmanisation was an era when the re-design of Paris was to begin to accommadate the speed of new Modernity. Paris was a socially desirable city and it was cleansed for Modernity.
Portraits by artists showed the alienation through Modernity and it's experience.
Physchology then emerges in 1893, with the technological wonders and when people started to worry about the speed of ageing. Modernism speeded up our lives but also made us more distracted. It condenced social spaces also making poeple more competative and had them making direct attemts to make themselves look better by engaging with the new technologies and the new way of living.
It invented things like the Kaiserpanorama in 1883, which was a round viewing device that people could put money into and watch slides of erotica, art and pictures of the modern world. They ahd began to prefer to watch the world through new technologies rather than in a direct way.
Soon after cinema was invented and the first film by the Lumiere Brothers was shown. The film of a train coming into a station scared people in the first showing because they thought it was real life. People also started to see the world from a birds eye view which they found fascinating.
The Lumiere Brothers first film
- Monet's work reflected on the sensations of Modernity, and the Impressionists began to be influeneced by photography.
- The Flat Iron building in New York is a product of modernity, towering over nature, it is a rational piece of design.
Edward Muybridge created images where he was trying to understand ourselves in a scientific way.
There was then the stages of Anti-Historicism, which was about not looking backwards but fowards, and the idea in modern design with a principle to let modern materials speak for themselves. If a chair is metal then dont try and disguise it as wood etc.
There was the whole idea of truth to materials and form follow functions within design and the form of modern function should fit it's purpose.
- Internationalism was another part of modernity, where all modernists designs should be readable and understandable by anyone anywhere. It created a democratic international language.
In regards to truth to materials and that form follows function, pre 19th century cutlery was attempting to disguise materials, it had aspirations to be artistic, whereas Bauhaus cutlery followed the truth to material and that beauty comes from simplicity.
Adolf Loos in 1908, once said that the desire to decorate is the sign of the retarded delivery and backwardness... ornament is crime. He was also against tattoos as he didnt see the point in decorating ones self when the body is beautiful as it is.
Bauhaus was the most influential art school of the 19th century and was the main start and influence of Modernism, it taught and lived Modernism. It was an interdisciplinery school for modernist practitioners, modernising education.
The school was shut down by the Nazi's as they thought it was developing too quickly.
- The Bauhaus created designs that could be mass produced and available to all.
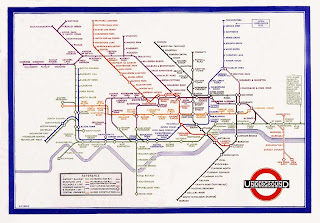
Harry Beck designed the London underground maps, he made them colour coded so that they could be read by anyone, he had an international ethos, fitting in with the idea of Internationalism.
In the same era as Modernism there began the developing of historical fonts again from the classical culture. The Times New Roman font was designed in 1932. Along with the Nazi's Fraktur font to show historical roots.




No comments:
Post a Comment